ATA Carnet (CBP CBSA): Difference between revisions
Created page with "{{note|This article is part of the Shipment Release Types Guide|info}} {{#ev:youtube|yvjb7iCJ6LY|360|right|How to create an ATA Carnet shipment in ACI using BorderConnect.}}An '''ATA Carnet''' is an international customs document that allows for the temporary importation of goods into a country. Because it is accepted in both Canada and the United States, it can act as a both a Canadian and U.S. Shipment Types For ACE and A..." |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{note|This article is part of the [[Shipment_Types_For_ACE_and_ACI_eManifest|Shipment Release Types Guide]]|info}} | {{note|This article is part of the [[Shipment_Types_For_ACE_and_ACI_eManifest|Shipment Release Types Guide]]|info}} | ||
{{#ev:youtube| | {{#ev:youtube|hOzdGq67ML8|960|center|How to create an ATA Carnet shipment in ACI using BorderConnect.}} | ||
An '''ATA Carnet''' is an international customs document used to simplify '''temporary admission''' (temporary import/export) of eligible goods. In Canada, carnets are an alternative to documenting temporary importations on form E29B (Temporary Admission Permit), and they act as a guarantee for duties/taxes if the goods are not re-exported within the authorized time limits.<ref name="cbsa-d8-1-7">CBSA Memorandum D8-1-7 — ''Use of A.T.A. Carnets and Canada/Chinese Taipei Carnets for the Temporary Admission of Goods'' https://www.cbsa-asfc.gc.ca/publications/dm-md/d8/d8-1-7-eng.html</ref> | |||
The | Carnets are typically used for '''commercial samples''', '''professional equipment''', and '''goods for exhibitions/fairs'''. Carnets generally cannot be used for goods intended for sale, lease, processing, repair, or for consumable goods (e.g., food/plants) that may be used up or disposed of.<ref name="cbsa-d8-1-7" /> | ||
Carnets are issued by recognized issuing organizations (not by CBSA). In Canada, carnets are guaranteed by the Canadian Chamber of Commerce and are obtained through carnet service providers/issuing offices.<ref name="cbsa-d8-1-7" /> | |||
'''Validity / time limits:''' Carnets are valid for '''one year from the date of issue''', but the '''authorized period of stay''' in Canada can be shorter if CBSA sets an earlier re-exportation date on the importation counterfoil. Duties and taxes may apply if goods are not re-exported within the authorized time limits (including if the carnet expires).<ref name="cbsa-d8-1-7" /> | |||
The carnet should be obtained by the party temporarily importing the goods (the carnet holder). The carrier/driver must have the carnet available to present to border officials when reporting the goods.<ref name="cbsa-d8-1-7" /> | |||
== Declaring an ATA Carnet in ACI eManifest == | == Declaring an ATA Carnet in ACI eManifest == | ||
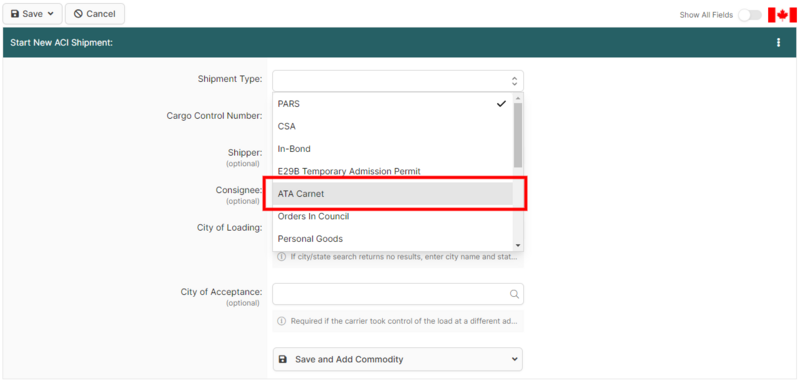
Carnet | Carnet shipments transported by highway into Canada must still be reported to CBSA under ACI/eManifest using a Highway Cargo Document (cargo control document) within the required timelines (generally validated at least one hour prior to arrival at the first port of arrival).<ref name="cbsa-eccrdhi">CBSA — ''ACI/eManifest Highway Electronic Commerce Client Requirements'' https://www.cbsa-asfc.gc.ca/prog/manif/eccrdhi-deccerout-eng.html</ref> To report an ATA Carnet the carrier will need to create an ACI Shipment designated as non-CSA (or "ATA Carnet" if using [https://borderconnect.com/ BorderConnect's] [[ACI eManifest Software User Guide (CBSA)|ACI eManifest software]]), and ensure that the shipment is transmitted as part of their ACI eManifest. | ||
[[Image:Atacarnet1.png|800px]] | [[Image:Atacarnet1.png|800px]] | ||
| Line 15: | Line 21: | ||
Although an ATA Carnet Shipment is different from a [[PARS_(CBSA_Shipment_Type)|PARS]] shipment, the carrier will still need to provide a unique [[Cargo Control Number (Canadian Shipments)|Cargo Control Number]], as well as all other information normally required for an ACI Shipment including Shipper, Consignee and Commodity information. | Although an ATA Carnet Shipment is different from a [[PARS_(CBSA_Shipment_Type)|PARS]] shipment, the carrier will still need to provide a unique [[Cargo Control Number (Canadian Shipments)|Cargo Control Number]], as well as all other information normally required for an ACI Shipment including Shipper, Consignee and Commodity information. | ||
At the border, the driver must | At the border, the driver must present the '''ATA Carnet document''' to CBSA for processing/validation as directed by the officer. A paper A8A is '''not''' a standard requirement for carnet processing; A8A (in-bond cargo control document) is associated with '''in-bond movements'''. If the goods are moving in-bond (for example, unaccompanied carnet goods moving in bond to an office of destination), the movement must be handled according to CBSA’s carnet and in-bond procedures.<ref name="cbsa-d8-1-7" /> | ||
{{reminder|ACI/eManifest highway cargo and conveyance data must generally be received and validated by CBSA at least one (1) hour prior to arrival at the first port of arrival (FPOA).}} | |||
== ATA Carnet and the United States == | |||
CBP recognizes ATA carnets as a mechanism to temporarily import eligible goods into the United States under carnet procedures. CBP’s official ATA Carnet FAQ describes the carnet as simplifying CBP formalities for temporary importation and explains general carnet use/processing expectations at entry and re-exportation.<ref name="cbp-carnet-faq">CBP — ''ATA Carnet Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ's)'' https://www.cbp.gov/trade/programs-administration/entry-summary/ata-carnet-faqs</ref> | |||
CBP’s carnet regulations (19 CFR Part 114) specify the categories of goods that may be covered by an ATA carnet, including '''commercial samples''', '''professional equipment''', and '''exhibitions/fairs''' under the applicable international conventions.<ref name="cfr-114-22">19 CFR § 114.22 — ''Coverage of carnets'' (Cornell LII) https://www.law.cornell.edu/cfr/text/19/114.22</ref> | |||
== ATA Carnet and ACE truck eManifest (highway mode) == | |||
In the highway environment, carnet processing frequently involves presenting the carnet paperwork at the port for CBP validation and following the instructions of the port and the filer’s service provider. ACE highway filing guidance from service providers states that ATA carnet cargo may be submitted by processing an empty ACE Manifest (unless additional shipments are also present). | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 12:51, 20 January 2026
| This article is part of the Shipment Release Types Guide |
An ATA Carnet is an international customs document used to simplify temporary admission (temporary import/export) of eligible goods. In Canada, carnets are an alternative to documenting temporary importations on form E29B (Temporary Admission Permit), and they act as a guarantee for duties/taxes if the goods are not re-exported within the authorized time limits.[1]
Carnets are typically used for commercial samples, professional equipment, and goods for exhibitions/fairs. Carnets generally cannot be used for goods intended for sale, lease, processing, repair, or for consumable goods (e.g., food/plants) that may be used up or disposed of.[1]
Carnets are issued by recognized issuing organizations (not by CBSA). In Canada, carnets are guaranteed by the Canadian Chamber of Commerce and are obtained through carnet service providers/issuing offices.[1]
Validity / time limits: Carnets are valid for one year from the date of issue, but the authorized period of stay in Canada can be shorter if CBSA sets an earlier re-exportation date on the importation counterfoil. Duties and taxes may apply if goods are not re-exported within the authorized time limits (including if the carnet expires).[1]
The carnet should be obtained by the party temporarily importing the goods (the carnet holder). The carrier/driver must have the carnet available to present to border officials when reporting the goods.[1]
Declaring an ATA Carnet in ACI eManifest
Carnet shipments transported by highway into Canada must still be reported to CBSA under ACI/eManifest using a Highway Cargo Document (cargo control document) within the required timelines (generally validated at least one hour prior to arrival at the first port of arrival).[2] To report an ATA Carnet the carrier will need to create an ACI Shipment designated as non-CSA (or "ATA Carnet" if using BorderConnect's ACI eManifest software), and ensure that the shipment is transmitted as part of their ACI eManifest.
Although an ATA Carnet Shipment is different from a PARS shipment, the carrier will still need to provide a unique Cargo Control Number, as well as all other information normally required for an ACI Shipment including Shipper, Consignee and Commodity information.
At the border, the driver must present the ATA Carnet document to CBSA for processing/validation as directed by the officer. A paper A8A is not a standard requirement for carnet processing; A8A (in-bond cargo control document) is associated with in-bond movements. If the goods are moving in-bond (for example, unaccompanied carnet goods moving in bond to an office of destination), the movement must be handled according to CBSA’s carnet and in-bond procedures.[1]
| ACI/eManifest highway cargo and conveyance data must generally be received and validated by CBSA at least one (1) hour prior to arrival at the first port of arrival (FPOA). |
ATA Carnet and the United States
CBP recognizes ATA carnets as a mechanism to temporarily import eligible goods into the United States under carnet procedures. CBP’s official ATA Carnet FAQ describes the carnet as simplifying CBP formalities for temporary importation and explains general carnet use/processing expectations at entry and re-exportation.[3]
CBP’s carnet regulations (19 CFR Part 114) specify the categories of goods that may be covered by an ATA carnet, including commercial samples, professional equipment, and exhibitions/fairs under the applicable international conventions.[4]
ATA Carnet and ACE truck eManifest (highway mode)
In the highway environment, carnet processing frequently involves presenting the carnet paperwork at the port for CBP validation and following the instructions of the port and the filer’s service provider. ACE highway filing guidance from service providers states that ATA carnet cargo may be submitted by processing an empty ACE Manifest (unless additional shipments are also present).
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 CBSA Memorandum D8-1-7 — Use of A.T.A. Carnets and Canada/Chinese Taipei Carnets for the Temporary Admission of Goods https://www.cbsa-asfc.gc.ca/publications/dm-md/d8/d8-1-7-eng.html
- ↑ CBSA — ACI/eManifest Highway Electronic Commerce Client Requirements https://www.cbsa-asfc.gc.ca/prog/manif/eccrdhi-deccerout-eng.html
- ↑ CBP — ATA Carnet Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ's) https://www.cbp.gov/trade/programs-administration/entry-summary/ata-carnet-faqs
- ↑ 19 CFR § 114.22 — Coverage of carnets (Cornell LII) https://www.law.cornell.edu/cfr/text/19/114.22