Shipment Control Number (CBP)
| This article is part of the Customs Glossary Guide |
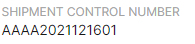
A Shipment Control Number (SCN) is a unique identifier assigned to a specific shipment or consignment of goods. It serves as a reference number used to track and manage shipments throughout the logistics and customs clearance processes. In the context of PAPS (Pre-Arrival Processing System) barcode labels, the SCN plays a vital role in streamlining and expediting the customs clearance of shipments entering the United States. This article defines the Shipment Control Number, explores its usage scenarios, and outlines its significant role in importing shipments to the U.S., particularly in the context of PAPS barcode labels.
What is a Shipment Control Number (SCN)?
A Shipment Control Number (SCN) is an alphanumeric code thaht starts with the highway carrier's four-letter Standard Carrier Alpha Code (SCAC) followed by a unique number and used to uniquely identify a particular shipment or consignment of goods. It is created and assigned by the shipping or logistics company responsible for transporting the goods. The SCN serves as a key reference for stakeholders involved in the movement of the shipment, including carriers, customs officials, freight forwarders, and importers.
Usage Scenarios of Shipment Control Number (SCN):
Containerized Cargo:
Scenario: An exporter in Asia is sending a containerized shipment of textiles to a U.S. importer. SCN Usage: The shipping company will generate an SCN for the specific container carrying the textiles. This SCN will be included in the shipping documents and PAPS barcode labels, allowing for seamless tracking and processing of the shipment upon arrival in the United States.
Less Than Container Load (LCL) Shipments:
Scenario: A manufacturer in Europe is shipping multiple small consignments of machine parts to various U.S. customers using an LCL service. SCN Usage: The logistics company handling the LCL shipments will assign a unique SCN to each individual consignment. The SCN will be encoded in the PAPS barcode labels attached to each shipment, facilitating efficient tracking and customs clearance upon entry to the United States. Air Cargo:
Scenario: An electronics manufacturer in South America is exporting a shipment of smartphones to a U.S. retailer via an air cargo carrier. SCN Usage: The air cargo carrier will create an SCN for the specific shipment of smartphones. This SCN will be encoded in the PAPS barcode labels affixed to the air waybill and other shipping documents, simplifying cargo handling and customs processing upon arrival in the U.S.
Role of Shipment Control Number (SCN) in PAPS Barcode Labels for Importing Shipments to the U.S.:
Streamlining Customs Clearance:
Including the SCN in PAPS barcode labels enables U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) officials to quickly retrieve shipment details from their system. This expedites the customs clearance process, reducing delays and ensuring efficient cargo handling.
Efficient Tracking and Visibility:
The SCN in PAPS barcode labels allows carriers, customs brokers, and importers to easily track and monitor the movement of shipments as they arrive at U.S. ports of entry. It enhances shipment visibility, promoting better supply chain management.
Compliance and Data Accuracy:
The use of the SCN in PAPS barcode labels ensures accurate shipment references, reducing the risk of data discrepancies and ensuring compliance with U.S. customs regulations. CBP can cross-reference the SCN to verify cargo details and confirm shipment information.
Enhanced Border Security:
The SCN on PAPS barcode labels aids in conducting risk assessments on incoming shipments, improving border security, and safeguarding against potential threats.
Conclusion
The Shipment Control Number (SCN) is a critical identifier used to uniquely distinguish shipments and consignments of goods. When included in PAPS barcode labels, the SCN streamlines customs clearance processes, enhances tracking and visibility, ensures compliance with customs regulations, and contributes to enhanced border security. By leveraging PAPS barcode labels with SCNs, importers and logistics companies can expedite the customs clearance of shipments entering the United States, promoting efficient and secure trade operations.
