CSA (CBSA Shipment Type)
|
🔖 This article is part of the Shipment Release Types Guide |
|
🔖 This article is about the CSA Shipment Type. For general program info, visit CSA Program Information |
CSA Shipment (Canada/CBSA)
A guide to the Customs Self-Assessment (CSA) program, a "Trusted Trader" option for streamlined border clearance.
Overview
CSA (Customs Self Assessment) is a clearance option designed for low-risk, pre-approved companies. It allows goods to enter Canada without standard border release processing (like PARS).
Instead of the broker clearing the goods at the border, the Importer self-assesses duties and taxes later. This means the driver can often pass through the booth simply by verifying their identity.
The "Triangle" Rule: CSA can only be used if all three parties are authorized: 1. The Importer (must be CSA approved). 2. The Carrier (must be CSA approved). 3. The Driver (must have a FAST or CDRP card).
✅ Eligibility & Restrictions
Not all goods qualify for CSA, even if the importer is approved.
| Requirement | Detail |
|---|---|
| Origin | Goods must be shipped directly from the United States or Mexico. |
| No OGDs | Goods cannot require permits, licenses, or certificates from other government departments (e.g., CFIA, NRC).[1] |
| Responsibility | The Importer is responsible for telling the carrier if a load is eligible for CSA. |
Two Ways to Report CSA
Carriers have two options for handling CSA shipments. Most use Option 1 (Exempt).
Option 1: Traditional (Exempt)
Most Common. CSA shipments are exempt from ACI eManifest data requirements.
- Manifest: You do not need to create an electronic manifest for these goods.
- Mixed Loads: If you have PARS and CSA on the same truck, you only manifest the PARS. The CSA goods remain "off the books" electronically.
- Border: The driver relies entirely on the 3 Barcodes (see below).
Option 2: Electronic (ACI)
Voluntary. Some carriers choose to transmit CSA data electronically for tracking visibility.
- Manifest: You create a manifest and add the shipment as type CSA.
- Setup: You must notify CBSA's Technical Support Unit before starting this.[2]
- Border: The driver presents the ACI Lead Sheet plus their FAST card.
At the Border (The 3 Barcodes)
The Paper Process
If using Option 1 (Traditional), the driver does not present a manifest lead sheet. Instead, they present three specific items to the officer:
1. The Driver's Card: A valid FAST or CDRP card (scanned first). 2. The Carrier Code: A barcode of the carrier's code. 3. The Importer's Business Number: A barcode of the Importer's CSA Business Number (BN).
Note: If any one of these three items is missing or invalid, the driver will be refused CSA clearance and must clear via the regular commercial lane (PARS).
Creating a CSA Shipment (Option 2)
If you choose to file electronically, follow these steps in BorderConnect.
1 Start New Shipment
Inside your ACI eManifest, click Create New Shipment.
- Shipment Type: Select CSA.
- Cargo Control Number: Enter a unique CCN (Carrier Code + Number).
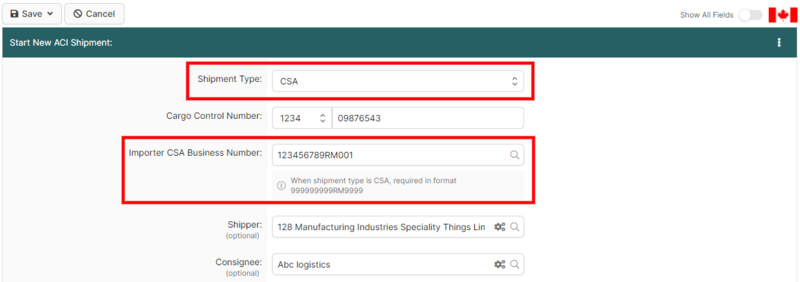
2 Complete & Transmit
- Enter the Shipper, Consignee, and Commodity details.
- Click Save.
- Click Sync with CBSA on the manifest page.
