Free of Duty (CBP Shipment Type)
|
🔖 This article is part of the Shipment Release Types Guide |
Free of Duty (CBP Form 7523)
A guide to processing duty-free informal entries for merchandise valued at $2,500 or less.
Overview
A Free of Duty shipment is a U.S. shipment type identified by CBP Form 7523 (Entry and Manifest of Merchandise Free of Duty). It is a type of Informal Entry that allows for the release of merchandise that is unconditionally or conditionally duty-free at the border.
To qualify for this release method, the shipment value must not exceed $2,500 USD. The goods must either be unconditionally duty-free (not subject to quota or internal revenue tax) or conditionally duty-free with all conditions met at the time of arrival.
Historical Manifest Note: Under 19 CFR § 123.4, CBP Form 7523 may historically be used as an inward foreign manifest in lieu of other forms in specific cases.
Electronic Filing Requirements
While some informal entries have specific exemptions, highway carriers are generally required to transmit advance electronic cargo information via an approved EDI system.
- ACE eManifest Status: Free of Duty shipments are often categorized by CBP as exempt from full mandatory ACE cargo filing.
- Best Practice: Carriers are strongly encouraged to submit ACE information to ensure faster border processing and maintain digital records.
- 19 CFR § 123.92: General truck rules require advance electronic information for truck cargo unless a specific mode-based exception applies.
Declaring in ACE eManifest
Step 1: Create the ACE Shipment
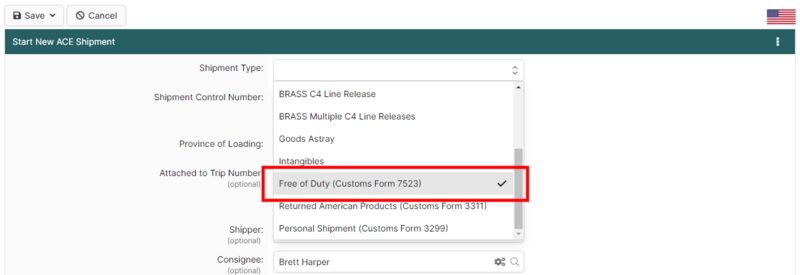
In BorderConnect, select Free of Duty (or "CBP Form 7523") as the Shipment Type.
- Shipment Control Number (SCN): Assign a unique SCN to the shipment.
- Data Elements: Provide all standard information, including Shipper, Consignee, and Commodity details.
- No Broker Required: As an informal entry, a customs broker is not involved, and no entry number is generated.

Step 2: At the Border
Even if an electronic manifest is filed, the physical paperwork is the primary release document.
- Physical Form: The driver must present two copies of a completed CBP Form 7523 to the officer at the booth.
- Identification: The driver should present the ACE lead sheet to allow the officer to locate the trip record in the manifest system.
References
